The 21st century has brought more natural 5 Critical Solutions disasters and environmental changes than ever before. As humans continue to consume more resources to meet growing material needs, natural resources are depleting rapidly. This overuse is harming the environment and making sustainability a major challenge.
To tackle this, the United Nations (UN) introduced Sustainable Development Goal 12 (SDG 12): Responsible Consumption and Production. This goal focuses on reducing waste, using resources wisely, and promoting sustainable business practices.
One of the biggest global challenges is how to meet the needs of a growing population while protecting the environment. To achieve this, industries must change their strategies and encourage minimal and responsible consumption. By doing so, businesses can help create a future where economic growth and environmental protection go hand in hand.
The challenge is immense. Balancing the growing demands of a global population with the imperative to protect our environment requires a fundamental shift in mindset. Industries must realign their strategies, embracing minimal consumption and prioritizing sustainable practices.
But this isn’t just a task for corporations and governments; it’s a collective responsibility, a call for each of us to become conscious consumers and responsible producers.So, how do we navigate this complex landscape and forge a path towards a sustainable future? Let’s delve into five critical solutions that can help us tackle global waste and build a more responsible and resilient world.
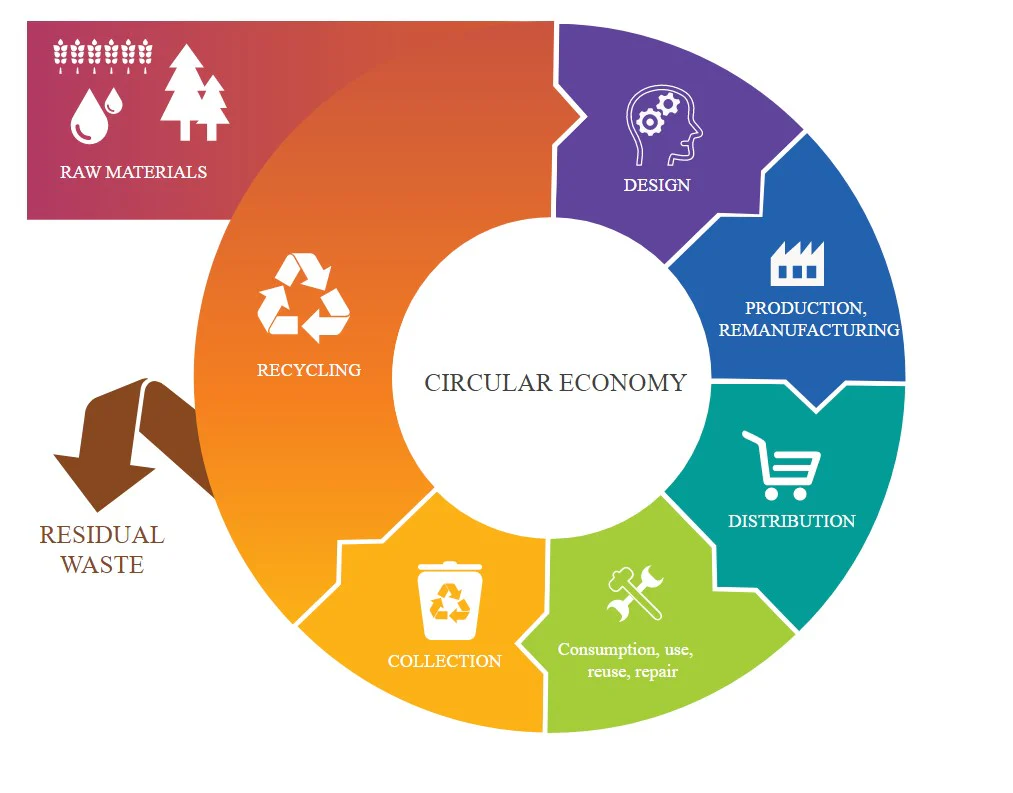
1. Embracing the Circular Economy: 5 Critical Solutions
The linear economy, with its emphasis on extraction, production, consumption, and disposal, is inherently wasteful.
The circular economy, on the other hand, envisions a closed-loop system where resources are kept in circulation for as long as possible 5 Critical Solutions.
It’s about designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability. It’s about transforming waste into valuable resources.
Imagine a world where:
Product design prioritizes longevity and repair: Products are built to last, not to be replaced every year. Modular design allows for easy repairs and upgrades, extending the lifespan of goods.
Recycling and upcycling are the norm: Waste is seen as a resource, not a problem. Advanced recycling technologies transform discarded materials into high-quality inputs for new products. Upcycling breathes new life into old items, turning them into unique and valuable creations.
Sharing and renting models flourish: Access trumps ownership. Sharing platforms and rental services allow us to enjoy the benefits of products without the burden of ownership, reducing the demand for new goods.
Industrial symbiosis becomes widespread: Industries collaborate to exchange byproducts and waste streams, creating closed-loop systems where one company’s waste becomes another’s resource.
The circular economy is not just an environmental imperative- it’s an economic opportunity. By embracing circular principles, businesses can reduce costs, create new revenue streams, and enhance their brand reputation..
2. Sustainable Production: Minimizing Environmental Footprint
Responsible consumption cannot exist without sustainable production. Businesses have a crucial role to play in minimizing their environmental footprint by adopting eco-friendly practices throughout their supply chains.
This includes:
Investing in renewable energy: Transitioning from fossil fuels to solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources reduces greenhouse gas emissions and mitigates climate change.
Implementing water conservation measures: Water is a precious resource, and industries must adopt water-efficient technologies and practices to minimize their water footprint.
Reducing waste and pollution: Implementing cleaner production processes, minimizing packaging, and managing waste responsibly can significantly reduce environmental impact.
Sourcing sustainable materials: Choosing materials from responsibly managed forests, recycled sources, and eco-friendly suppliers reduces the demand for virgin resources and minimizes environmental degradation.
Extending Producer Responsibility (EPR): Making producers responsible for the end-of-life management of their products incentivizes them to design for recyclability and durability.
Transparency and accountability are crucial for sustainable production. Businesses must track and report their environmental performance, allowing consumers to make informed choices 5 Critical Solutions.
3. Conscious Consumption: Empowering Informed Choices
Consumers are not passive recipients of products; they are active agents in shaping the market. By making conscious choices, 5 Critical Solutions we can drive demand for sustainable products and practices.
This involves:
Reducing consumption: Questioning our needs and wants, and opting for quality over quantity. Avoiding impulse purchases and 5 Critical Solutions embracing minimalism can significantly reduce our environmental footprint.
Choosing sustainable products: Looking for eco-labels and certifications that indicate products are made with sustainable materials and practices. Supporting businesses that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
Extending product lifespan: Repairing, reusing, and repurposing items instead of discarding them. Taking care of our belongings to prolong their lifespan.
Reducing food waste: Planning meals, buying only what we need, and composting food scraps can significantly reduce food waste, which has a massive environmental impact 5 Critical Solutions.
Supporting local and ethical businesses: Choosing products from local producers and businesses that prioritize fair labor practices and sustainable sourcing 5 Critical Solutions.
Education and awareness play a vital role in promoting conscious consumption. Consumers need access to information about the environmental and social impacts of their choices.
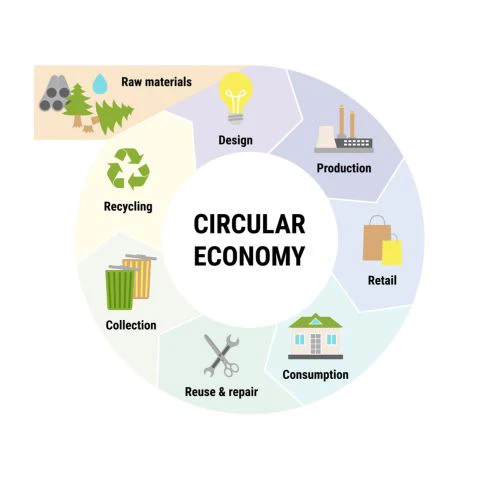
4. Technological Innovation: Enabling Sustainable Solutions
Technology can be a powerful tool for driving sustainable consumption and production. Innovations in materials science, renewable energy, and waste management can help us overcome environmental challenges.
This includes:Developing biodegradable and compostable materials: Replacing traditional plastics with bio-based materials that decompose naturally can reduce plastic pollution.
Advancing recycling technologies:5 Critical Solutions Developing more efficient and effective recycling processes can increase the recovery of valuable materials from waste streams.
Implementing smart technologies: Utilizing sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence to optimize resource use and reduce waste in production and consumption.
Promoting renewable energy technologies: Investing in research and development of solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies to accelerate the transition to a clean energy future.
Utilizing blockchain technology: Increasing transparency and traceability in supply chains, allowing consumers to verify the sustainability credentials of products 5 Critical Solutions.
Technological innovation alone is not enough.5 Critical Solutions It must be coupled with policy support, investment, and collaboration to achieve its full potential.


 Collaborating for a Sustainable Future: SDG17 in Focus | SDG Book Club
Collaborating for a Sustainable Future: SDG17 in Focus | SDG Book Club  Breaking Poverty: 10,000 Lives Empowered for a Brighter, Sustainable Future
Breaking Poverty: 10,000 Lives Empowered for a Brighter, Sustainable Future
good!
Super!
Good!
wonderful!