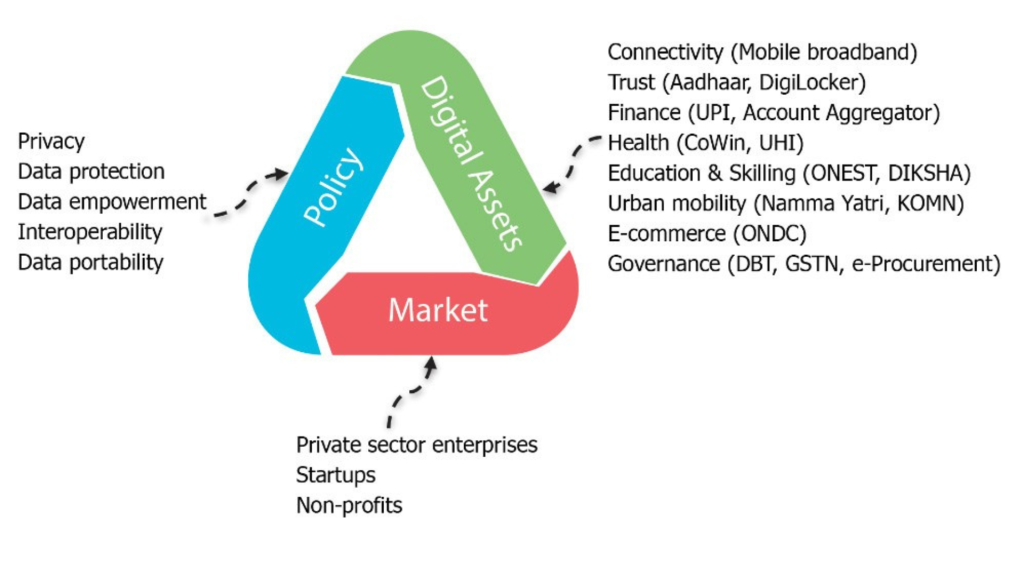
Over the last ten years, India has built a strong digital system called Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), which works for the whole population. The main parts of this system are called the India Stack. These include:
Aadhaar – a digital ID for every citizen
Jan Dhan – a program to help people open bank accounts
UPI – a system that makes digital payments easy and fast
India Stack also supports improvements in health, education, job skills, and even future plans for digital travel and shopping.
India made rules that protect people’s data, Public Infrastructure allow different digital tools to work together, and support private businesses. This helped grow the market for many services and goods. Thanks to this system, more people now have access to banking, which also helps India move faster towards global goals like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
One big reason countries should invest in DPI is that it helps create new businesses and jobs. DPI can encourage startups and private investors to create local solutions. But to make this work, governments need to support it with the right rules and systems. India’s experience shows that the Public Infrastructure government can help both control and grow the digital space—especially in key areas like banking and finance.
India’s DPI played a key role in changing the financial sector. In 2011, only about 1 in 3 people above age 15 had a bank account. By 2021, almost everyone had one. This change happened because of tools like Aadhaar’s e-KYC, which helps open bank accounts easily. Another big change came in 2016 with UPI, a simple, fast, and secure way to send and receive money. Public Infrastructure UPI made India one of the top countries in the world for digital payments.
With a strong digital base, India became a center for innovation in digital finance and technology, also known as fintech.
However, people outside India may not fully understand how its rules and policies helped private ,Public Infrastructurecompanies invest. This paper looks at that. First, it explains how the public and private sectors can work together to create innovation using DPI. Then it talks about India’s policies that helped more people join the financial system and encouraged investment in new digital products and services. Finally, it shares lessons from India to help other countries build their own DPI systems.
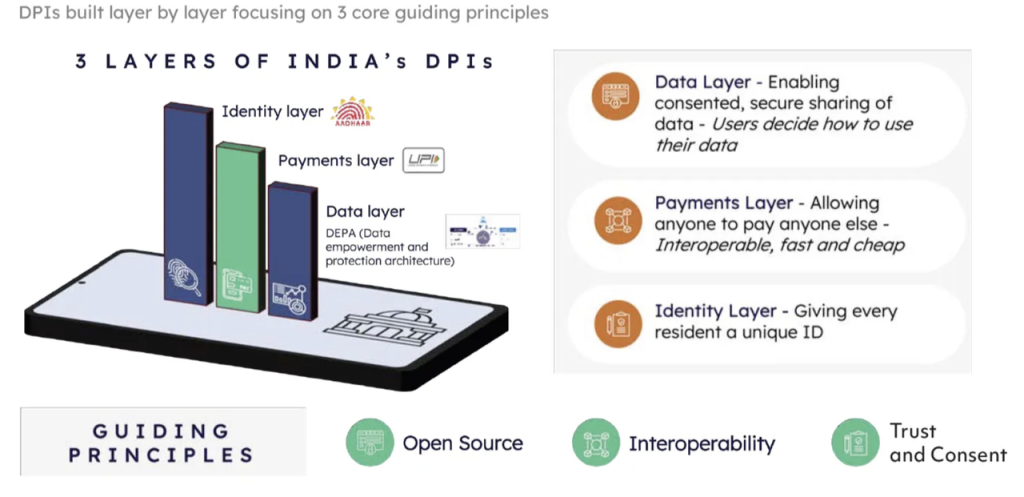
The Journey: Aadhaar to India Stack

India’s DPI journey began with Aadhaar in 2009. The goal was to build basic digital tools that help deliver services to everyone through cheap and widely available internet or mobile networks. Aadhaar’s open and flexible design allowed different technologies to work together. Public Infrastructure These formed the “India Stack,” which has three main layers:
Identity – Aadhaar for digital ID
Payments – systems like UPI
Data – tools to share and use data securely with user permission
These tools let the government, companies, and developers build services that don’t need paper or in-person visits, and still keep user consent.
To make DPI work well, India also invested in internet access and made digital services cheap and simple to use, even for people not used to digital tools. Public Infrastructure Technologies like Aadhaar and digital data sharing help check and approve payments securely. Public money helped make these services available even in remote areas. This encouraged private businesses to come in and build more services.
For DPI to fully help with financial inclusion, businesses need to see real chances to build new products for people who were left out before. For example, small insurance products for low-income groups can bring in many new customers. Public Infrastructure With good rules and support, countries can draw private money to grow financial services, making it a win for everyone.
1. Lowering the Entry Barrier: Public Infrastructure
Starting a business can be tough. You need to deal with paperwork, set up payment systems, and find ways to reach customers. DPI can take away a lot of these headaches.
Digital Identity: dream a system where everyone has a secure digital ID. This means businesses can easily verify customers online, reducing fraud and making it easier to onboard new users.
A small shop in a village can now sell to customers across the country with confidence.
Unified Payment Interfaces: A simple, open payment system means businesses don’t have to build their own payment infrastructure.
They can just plug into the existing system, saving time and money. This is especially helpful for small businesses that don’t have a lot of resources.
Data Sharing Platforms: DPI can create platforms where data can be shared securely and easily. This lets businesses access information they need to make better decisions, develop new products, and reach new markets. For example, a farmer could use data about weather and soil conditions to improve their crops Public Infrastructure.
2. Boosting Efficiency: Doing More with Less
DPI can make everyday business operations smoother and faster.
Automation: By automating tasks like invoicing and record-keeping, businesses can save time and reduce errors. This frees up employees to focus on more important things, like innovation and customer service.
Streamlined Processes: DPI can help businesses connect with government services more easily. For example, filing taxes or applying for permits can be done online, saving time and reducing bureaucracy.
Real-Time Data: Access to real-time data about markets, customers, and supply chains can help businesses make smarter decisions. This can lead to better products, lower costs, and increased profits.
3. Fostering Inclusion: Reaching the Unreached
DPI can help bring the benefits of the digital economy to everyone, including those who have been left behind.
Financial Inclusion: Digital payment systems can help people who don’t have bank accounts access financial services. This can help them save money, borrow money, and start businesses.
Access to Markets: Online marketplaces can connect small businesses in rural areas with customers all over the country. This can help them grow and create jobs.
Digital Literacy: DPI can be used to provide digital literacy training to people who are not familiar with technology. This can help them participate in the digital economy.
4. Sparking Innovation: Building New Products and Services
DPI can create a fertile ground for innovation by providing a platform for businesses to build new products and services.
Open APIs: Open Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allow businesses to access and use data and services from other organizations. This can lead to the development of new and innovative applications.
Sandboxes: Sandboxes are safe environments where businesses can experiment with new technologies and ideas without taking on too much risk.
Hackathons and Competitions: DPI can be used to organize hackathons and competitions that encourage developers to create new solutions to real-world problems.
5. Building Trust: Creating a Safe and Secure Digital Environment
Trust is essential for a thriving digital economy. DPI can help build trust by providing a safe and secure digital environment.
Data Privacy and Security: DPI systems can be designed with strong security measures to protect user data. This is essential for building trust and encouraging people to use digital services.
Transparency and Accountability: DPI systems should be transparent and accountable. This means that users should be able to see how their data is being used and that there are mechanisms in place to ensure that the system is being used fairly.
Interoperability: DPI systems should be interoperable, meaning that they can work together seamlessly. This is essential for creating a connected and efficient digital economy.
The Bumps in the Road: Challenges and Considerations
While DPI offers immense potential, we need to be aware of the challenges:
Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring that user data is protected is crucial. We need strong regulations and safeguards to prevent data breaches and misuse.
Digital Divide: Not everyone has access to the internet or the skills to use digital technologies. We need to bridge the digital divide to ensure that everyone can benefit from DPI.
Interoperability: Making sure that different DPI Public Infrastructure systems can work together is a complex technical challenge. We need to develop open standards and protocols to Public Infrastructure ensure interoperability.
Governance and Regulation: Public Infrastructure We need clear and effective governance and regulatory frameworks to ensure that DPI is used fairly and responsibly.
Sustainability: Building and maintaining DPI requires significant investment. Public Infrastructure We need to ensure that DPI is sustainable in the long term.
Misuse of DPI: Systems that are built with good intent can be used by bad actors. Strong safeguards are needed to prevent this.
Building a Digital Future for All
DPI is not just about technology. It’s about creating a more inclusive, efficient, and innovative digital economy. By addressing the challenges and working together, governments, businesses, and civil society can harness the power of DPI to build a better future for everyone Public Infrastructure.

 5 Key Lessons from India’s Fintech Boom: How Digital Public Infrastructure Became a Catalyst for Private Sector Innovation
5 Key Lessons from India’s Fintech Boom: How Digital Public Infrastructure Became a Catalyst for Private Sector Innovation
good!
wonderful!