Our planet is an amazing place, full of different kinds of life. From the smallest bugs to the biggest whales, this variety of life is called biodiversity Breakdown. It’s like a giant, beautiful puzzle where every piece every plant, every animal, every tiny organism has a role to play. This biodiversity is not just pretty to look at – it’s essential for our survival. It gives us the air we breathe, the food we eat, the medicines we use, and so much more.
But this incredible web of life is facing some serious challenges. We are seeing a biodiversity breakdown, meaning that the number and types of living things are decreasing at an alarming rate.
However, it’s not all doom and gloom. While the threats are real and significant, there are also amazing efforts happening around the world to protect and restore biodiversity.
Five Rays of Hope – Positive Biodiversity Breakdown
Even as we face significant losses, there are inspiring stories of successful conservation and restoration. These triumphs show us that change is possible when people work together and dedicate themselves to protecting nature.
1. The Return of the Giants: Whale Populations Rebound
Many species were pushed to the brink of extinction. The International Whaling Commission (IWC) implemented a moratorium (a temporary ban) on commercial whaling in 1986, a landmark decision for marine conservation.
Humpback whales, for example, once numbered only a few thousand. Biodiversity Breakdown Today, thanks to protection efforts, their populations have rebounded significantly in many parts of the world. Similarly, gray whales, after facing near extinction in the Pacific, have been removed from the endangered species list.
This success story highlights the power of international Biodiversity Breakdown cooperation and strong protective measures. It shows that even for species facing dire situations, recovery is possible with dedicated effort and time.
2. Protecting Precious Places: The Growth of Protected Areas
One of the most effective ways to safeguard Biodiversity Breakdown is by creating protected areas. These are designated regions where human activities are restricted to conserve the natural environment and the species that live there.
Over the past few decades, there has been a significant increase in the number and size of protected areas around the globe. Governments, communities, and conservation organizations have worked together to set aside crucial habitats, from rainforests teeming with life to coral reefs bursting with color.
These protected areas provide safe havens for endangered species, allowing their populations to recover. They also help to preserve vital ecosystems, ensuring the continuation of important natural processes like water purification and carbon storage.
3. Bringing Back the Wild: Successful Reintroduction Programs
Sometimes, when a species has disappeared from a particular area, careful efforts can bring them back. Reintroduction programs involve breeding animals in captivity or relocating them from healthy populations to areas where they once lived.
There have been many successful reintroduction stories. For example, the Arabian Oryx, a majestic desert antelope, was once extinct in the wild. Through captive breeding programs and careful reintroduction efforts, this iconic species now roams free in several protected areas in the Middle East.
Similarly, the California Condor, a large scavenger bird, was on the brink of extinction with only a few dozen individuals left. An intensive captive breeding and release program has slowly brought their numbers back up. These programs are often complex and require long-term commitment, but they demonstrate that we can reverse some of the damage caused by human activities.
4. Indigenous Wisdom: Recognizing the Role of Local Communities
They possess a wealth of traditional knowledge about local ecosystems and sustainable resource management. Increasingly, conservation efforts are recognizing and valuing this knowledge.
Empowering these communities to manage their ancestral lands often leads to better protection of biodiversity, as they have a deep cultural and economic stake in its preservation Biodiversity Breakdown.
Recognizing the rights and knowledge of indigenous peoples is not just a matter of fairness; it’s a crucial element in effective and long-lasting conservation.
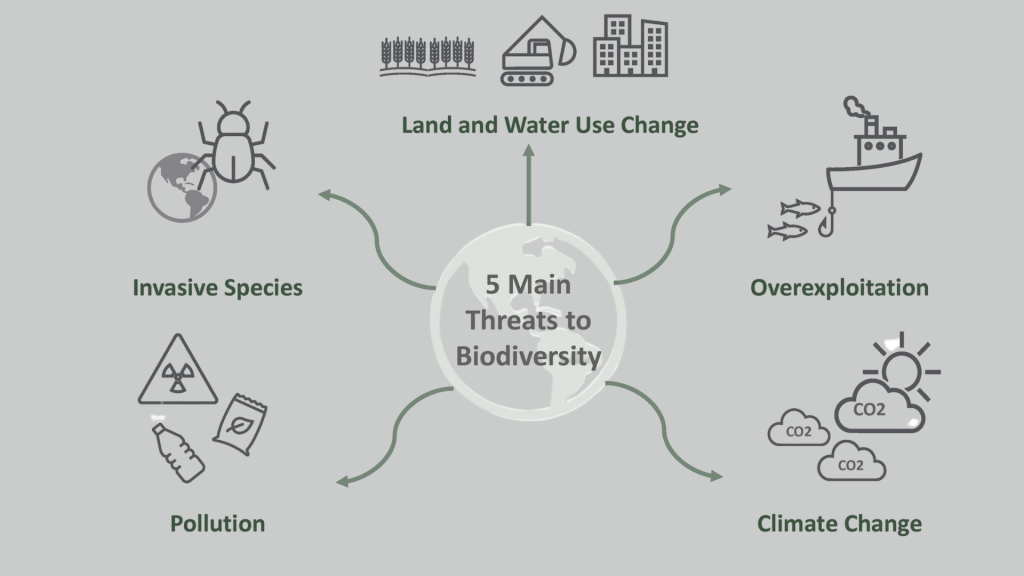
5. Technological Tools: Innovation for Conservation
Advances in technology are providing new and powerful tools for biodiversity conservation. From satellite imagery that helps monitor deforestation and track animal movements to DNA analysis that can identify endangered species and combat illegal wildlife trade, technology is playing an increasingly important role.
Drones are being used to survey wildlife populations and monitor remote areas. Acoustic monitoring devices can record animal sounds to track their presence and behavior. Artificial intelligence is being applied to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict threats to biodiversity.
These technological innovations are helping scientists, conservationists, and policymakers to better understand and address the challenges facing our planet’s biodiversity. Biodiversity Breakdown They offer new ways to monitor, protect, and manage natural resources more effectively.
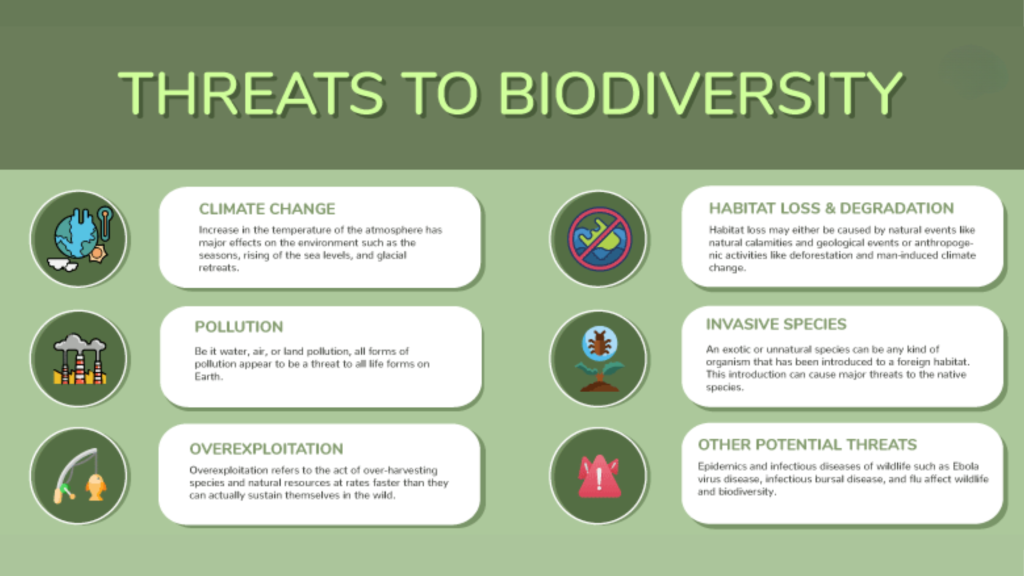
Three Storm Clouds on the Horizon – Critical Threats to Biodiversity
Despite the positive progress in some areas, significant threats continue to drive biodiversity loss worldwide. Addressing these challenges is crucial for safeguarding the future of life on Earth.
1. Habitat Destruction: The Relentless Loss of Natural Spaces

As human populations grow and our demand for resources increases, natural landscapes are being converted for agriculture, urbanization, infrastructure development, and resource extraction.
This habitat loss directly eliminates the places where plants and animals live,Biodiversity Breakdown leading to population declines and extinctions.
Furthermore, when large habitats are broken down into smaller, isolated patches (habitat fragmentation), it restricts the movement of animals, reduces genetic diversity, and makes populations more vulnerable to local extinction.
2. Climate Change: A Global Disruptor
Climate change, driven by the burning of fossil fuels and other human activities, is rapidly altering the Earth’s climate patterns. These changes have profound impacts on biodiversity. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation
3. Pollution: Poisoning Our Planet
Pollution, in its various forms, poses a significant threat to biodiversity. Biodiversity Breakdown Chemical pollutants from industrial activities and agriculture can contaminate water, soil, and air, harming or killing organisms directly and disrupting ecosystems.
Plastic pollution, particularly in the oceans, is a growing crisis. Marine animals can ingest or become entangled in plastic debris, leading to injury, starvation, and death. Microplastics are entering the food chain, with unknown long-term consequences for both wildlife and human health.
Nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff can create dead zones in aquatic ecosystems, where oxygen levels are too low to support life. Noise and light pollution can also disrupt animal behavior and communication. Reducing pollution at its source and finding more sustainable waste management practices are crucial for protecting Biodiversity Breakdown.
Conclusion:
The biodiversity breakdown is a serious challenge that demands our urgent attention. While the threats are significant and the losses are real, the positive triumphs highlighted in this blog offer a glimmer of hope. They show that conservation efforts can be effective when driven by dedication, collaboration, and innovation.


 What to Expect If a Small Asteroid Hits Earth.
What to Expect If a Small Asteroid Hits Earth.
good!
wonderful!
wonderful!
wonderful!