India, a nation on the cusp of rapid economic growth, faces the pressing challenge of balancing energy demands with environmental sustainability. While renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are gaining traction, biomass presents a unique and compelling opportunity – a domestically abundant, carbon-neutral resource with the potential to significantly contribute to the country’s energy mix.
What is Biomass?
Biomass refers to any organic matter derived from living or recently living organisms. This encompasses a diverse range of materials, including:
- Agricultural Residues:
- Crop Residues: Rice straw, wheat straw, sugarcane bagasse, corn stover, cotton stalks. These residues are abundant byproducts of agricultural activities and represent a significant source of biomass.
- Forestry Waste:
- Wood Waste: Sawdust, wood chips, bark, and other wood processing residues.
- Logging Residues: Branches, stumps, and other materials left behind during logging operations.
- Forest Thinning Debris: Material removed during forest thinning operations to improve forest health.
- Animal Waste:
- Manure: Cow dung, poultry litter, and other animal excreta.
- Animal Carcasses: Properly processed animal remains can be utilized for energy production.
- Municipal Solid Waste:
- Organic Components: Food scraps, yard waste (leaves, grass clippings), and other biodegradable materials from households and businesses.
- Aquatic Biomass:
- Algae: High-energy biomass that can be cultivated in water bodies.
- Seaweed: A renewable marine resource with potential for bioenergy production.
- Energy Crops:
- Dedicated Energy Crops: Specifically grown crops for energy production, such as switchgrass, miscanthus, and willow.
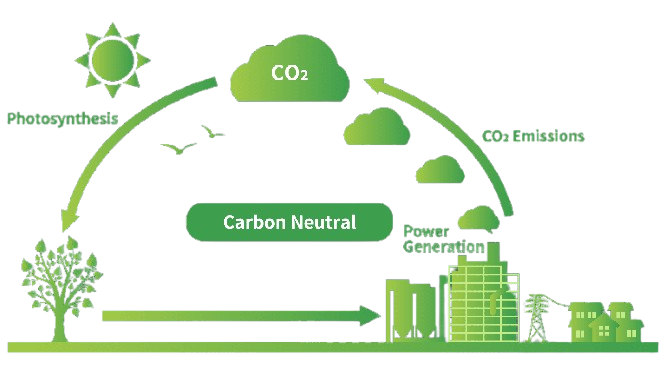
Why Biomass for India?
- Abundant Availability: India possesses a vast agricultural sector, generating a significant amount of agricultural residues annually. This abundance of biomass provides a readily available and domestically sourced energy resource.
- Rural Development: Biomass energy technologies, particularly decentralized ones like biogas plants and small-scale power generation units, can create employment opportunities and stimulate economic growth in rural areas.
- Waste Management: Utilizing agricultural and other organic waste for energy production addresses the pressing issue of waste management and reduces environmental pollution.
- Carbon Neutrality: When biomass is sustainably sourced and utilized, it is considered carbon-neutral. The carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during photosynthesis.
- Energy Security: By diversifying its energy mix, India can reduce its reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security and independence.
- Decentralized Energy Solutions: Biomass technologies can provide energy solutions to remote and off-grid communities, improving access to electricity and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Biomass Energy Products and Technologies:
- Biogas:
- Production: Anaerobic digestion of organic waste (animal manure, crop residues, food waste) produces biogas, a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide.
- Applications: Biogas can be used for cooking, heating, lighting, and even electricity generation through biogas engines.
- Products: Biogas digesters (batch and continuous flow), biogas upgrading systems (to increase methane content).
- Bioenergy for Electricity Generation:
- Direct Combustion: Biomass can be directly burned in boilers to generate steam, which drives turbines to produce electricity.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a combustible gas (syngas) through a process called gasification. Syngas can then be used to fuel gas engines or turbines for electricity generation.
- Pyrolysis: Biomass is heated in the absence of oxygen, producing biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
- Products: Biomass boilers, gasifiers, pyrolysis plants, power plants.
- Biofuels:
- Ethanol: Produced from starchy crops like corn or sugarcane.
- Biodiesel: Produced from vegetable oils and animal fats.
- Bioethanol: Produced from cellulosic biomass (lignocellulosic materials like wood, agricultural residues).
- Products: Biorefineries, ethanol plants, biodiesel production units.
- Biochar:
- Production: Pyrolysis of biomass produces biochar, a carbon-rich material with soil amendment properties.
- Applications: Improves soil fertility, enhances carbon sequestration, and can be used as a fuel source.
- Products: Pyrolysis reactors, biochar production units.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Sustainable Sourcing: Ensuring sustainable sourcing of biomass is crucial to avoid deforestation, land degradation, and competition with food production.
- Technology Development: Continuous research and development are needed to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass conversion technologies.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in infrastructure for biomass collection, transportation, and processing are essential for the successful deployment of biomass energy projects. This includes:
- Supply Chains: Establishing efficient and cost-effective supply chains for collecting and transporting biomass from farms and other sources to processing facilities.
- Storage and Handling: Developing appropriate storage and handling facilities to ensure the quality and prevent degradation of biomass feedstocks.
- Policy Support: Government policies and incentives, such as:
- Subsidies: Financial incentives for biomass energy projects.
- Feed-in Tariffs: Guaranteed prices for electricity generated from biomass.
- Tax Breaks: Tax incentives for investments in biomass energy technologies.
- Land Use Policies: Policies that promote sustainable land use practices and encourage the cultivation of energy crops.
- Skill Development: Training and capacity building programs are needed to develop a skilled workforce in biomass energy technologies, including operation, maintenance, and research.
Government Initiatives:
The Indian government has recognized the potential of biomass energy and has implemented several initiatives to promote its development, including:
- National Policy on Biofuels: This policy aims to promote the production and use of biofuels in India, including ethanol and biodiesel.
- National Bioenergy Mission: This mission focuses on promoting research, development, and deployment of bioenergy technologies, including biogas, biofuels, and biomass power generation.
- Subsidies and Incentives: Various subsidies and incentives are offered to encourage the development and deployment of biomass-based power plants, biogas plants, and biofuel production facilities.
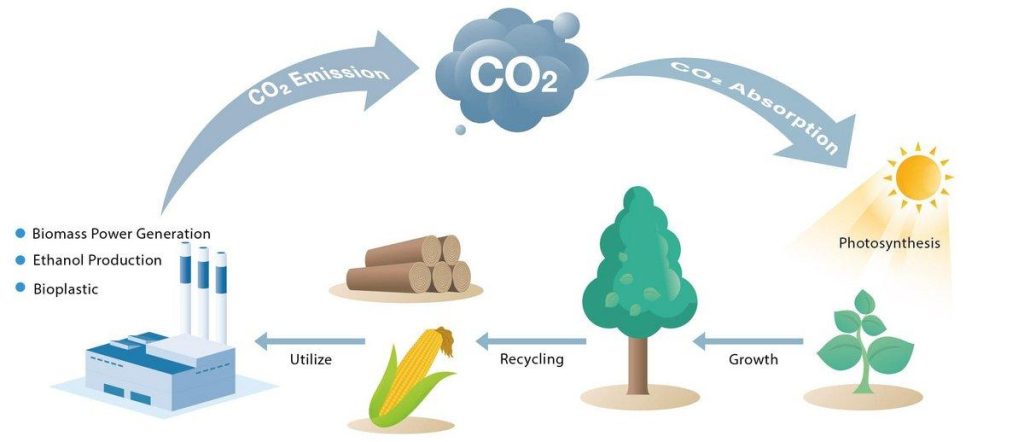
Case Studies:
- Successful implementation of biogas plants in rural areas: Many rural households and communities in India have successfully adopted biogas plants, providing them with clean cooking fuel, improving sanitation, and generating organic fertilizer.
- Large-scale biomass power plants: Several large-scale biomass power plants are operational in India, contributing to the country’s renewable energy generation capacity.
- Biofuel blending programs: The government has implemented programs to blend ethanol with gasoline, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
The Future of Biomass in India:
Biomass has the potential to play a significant role in India’s transition to a clean energy future. By addressing the challenges and capitalizing on the opportunities, India can unlock the full potential of biomass and contribute to a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future.
Key Considerations for the Future:
- Research and Development: Continued investment in research and development is crucial to improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biomass conversion technologies, such as advanced gasification and pyrolysis systems.
- Technological Innovation:
- Developing innovative technologies for biomass feedstock pretreatment, which can improve the efficiency of biomass conversion processes.
- Exploring new biomass feedstocks, such as algae and microalgae, which can offer high energy yields and potential for sustainable cultivation.
- Sustainable Land Use Planning: Ensuring sustainable land use practices for biomass feedstock production, avoiding deforestation, and minimizing competition with food production.
- Public Awareness and Education: Raising public awareness about the benefits of biomass energy and promoting its sustainable utilization.
Conclusion:
Biomass presents a promising avenue for India to achieve its energy and environmental objectives. With a focus on sustainable sourcing, technological advancements, supportive policies, and public awareness, India can harness the power of biomass to create a cleaner, greener, and more energy-independent future.


 Pre-Budget Insights from Mr. Amit Sharma, MD & CEO of Tata Consulting Engineers…
Pre-Budget Insights from Mr. Amit Sharma, MD & CEO of Tata Consulting Engineers…  Sultan Iskandar Thermal Power Station :- Powering Progress with Thermal Energy…
Sultan Iskandar Thermal Power Station :- Powering Progress with Thermal Energy…