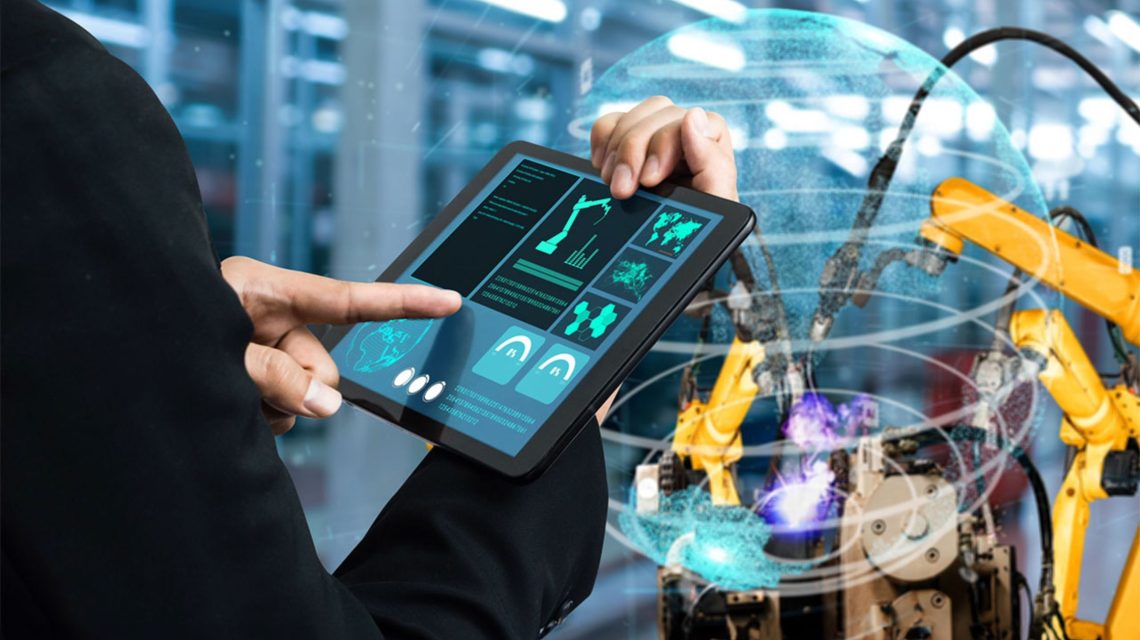
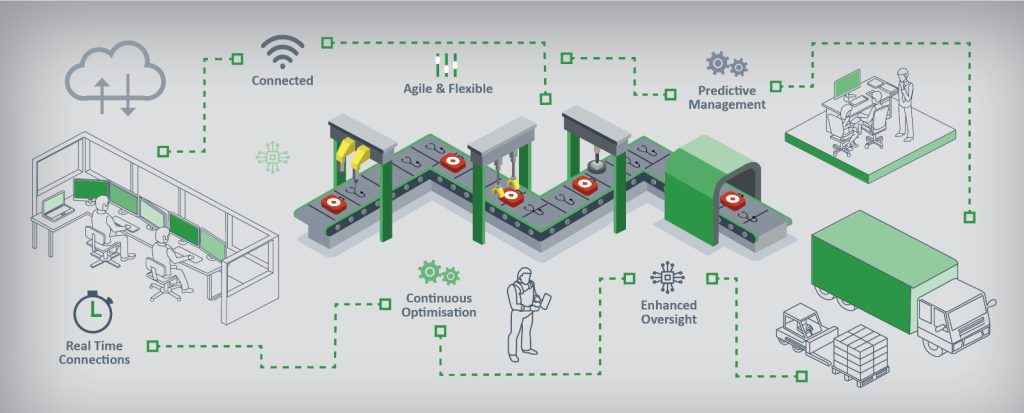
The manufacturing landscape is undergoing a radical transformation. Driven by the convergence of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and big data analytics, smart manufacturing is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day reality. This paradigm shift is revolutionizing how factories operate, enabling them to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and agility. This comprehensive blog post delves deep into the world of smart manufacturing, exploring its core components, benefits, challenges, and the strategies for successful implementation.
Understanding Smart Manufacturing:-
Smart manufacturing, at its core, represents the integration of digital technologies throughout the manufacturing process. It’s about connecting machines, processes, and people to create a highly networked and data-driven environment. This interconnectedness allows for real-time data collection, analysis, and informed decision-making, leading to optimised operations and improved outcomes. Several key technologies underpin the smart manufacturing revolution:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, including sensors, actuators, and connected machines, collect vast amounts of data from the factory floor. This data provides valuable insights into machine performance, production processes, and overall operational efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms analyze the data collected by IoT devices to identify patterns, predict failures, optimize processes, and automate tasks. This enables manufacturers to make data-driven decisions and improve efficiency in real-time.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure for storing, processing, and accessing the massive amounts of data generated in a smart manufacturing environment. Cloud computing also enables scalability and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to easily adjust their resources as needed.
- Big Data Analytics: Big data analytics tools are used to process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices and other sources. This analysis provides valuable insights into production processes, enabling manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and optimize their operations.
- Cybersecurity: As manufacturing becomes increasingly connected, cybersecurity becomes paramount. Protecting sensitive data and critical infrastructure from cyber threats is essential for maintaining operational integrity and preventing costly disruptions.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): 3D printing enables on-demand production of customized parts and products, reducing lead times and inventory costs. It also facilitates rapid prototyping and innovation.
- Digital Twin Technology: A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical asset, process, or system. Digital twins can be used to simulate different scenarios, optimize performance, and predict failures, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime.
The Benefits of Smart Manufacturing:-
The adoption of smart manufacturing solutions offers a wide range of benefits for manufacturers:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Real-time data insights enable manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and reduce downtime, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Costs: Smart manufacturing can help reduce costs by optimizing resource utilization, minimising waste, and improving maintenance practices.
- Improved Product Quality: Data-driven insights can be used to identify and address quality issues early in the production process, leading to improved product quality and reduced scrap rates.
- Enhanced Agility and Responsiveness: Smart manufacturing enables manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in demand and market conditions, improving agility and competitiveness.
- Increased Innovation: By facilitating rapid prototyping and experimentation, smart manufacturing fosters innovation and enables manufacturers to bring new products to market faster.
- Improved Safety: Smart manufacturing can improve safety by automating hazardous tasks, monitoring equipment performance, and identifying potential safety hazards.
- Enhanced Supply Chain Management: Smart manufacturing can improve supply chain visibility and optimize logistics, leading to reduced lead times and improved delivery performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Smart manufacturing provides manufacturers with access to vast amounts of data, enabling them to make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
Challenges of Smart Manufacturing Implementation:-
While the benefits of smart manufacturing are significant, implementing these solutions can also be challenging:
- High Initial Investment: Implementing smart manufacturing solutions often requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating different systems and technologies can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Data Security Concerns: As manufacturing becomes more connected, data security becomes a major concern. Protecting sensitive data from cyber threats is crucial.
- Skills Gap: Implementing and managing smart manufacturing solutions requires a skilled workforce with expertise in areas like data analytics, AI, and cybersecurity.
- Resistance to Change: Implementing smart manufacturing can involve significant changes to existing processes and workflows, which can be met with resistance from employees.
- Lack of Standardization: The lack of standardization in smart manufacturing technologies can make integration and interoperability challenging.
Strategies for Successful Smart Manufacturing Implementation:-
To successfully implement smart manufacturing solutions, manufacturers need to develop a comprehensive strategy that addresses the key challenges and leverages the potential benefits. Here are some key strategies for successful implementation:
- Develop a Clear Vision and Strategy: Define clear goals and objectives for smart manufacturing implementation and develop a roadmap for achieving them.
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: Don’t try to implement everything at once. Start with a pilot project and gradually scale up as you gain experience and refine your approach.
- Focus on Key Use Cases: Identify specific use cases that will deliver the greatest value and focus on implementing solutions for those areas first.
- Invest in Data Infrastructure: Build a robust data infrastructure to collect, store, and process the vast amounts of data generated in a smart manufacturing environment.
- Develop a Skilled Workforce: Invest in training and development to equip your workforce with the skills needed to manage and utilize smart manufacturing technologies.
- Address Cybersecurity Concerns: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
- Foster a Culture of Innovation: Encourage experimentation and innovation to explore new ways of using smart manufacturing technologies to improve operations.
- Collaborate with Partners: Partner with technology providers, consultants, and other organizations to leverage their expertise and accelerate your smart manufacturing journey.
- Embrace Agile Methodologies: Use agile methodologies to implement smart manufacturing solutions in an iterative and flexible manner.
- Measure and Track Progress: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your smart manufacturing initiatives and track progress over time.
The Future of Smart Manufacturing:-
Smart manufacturing is an evolving field, and the future holds even greater potential. As technologies continue to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated and transformative applications of smart manufacturing. Some key trends to watch include:
- The Rise of the Industrial Metaverse: The metaverse, a shared virtual world, is expected to have a significant impact on manufacturing. Manufacturers can use the metaverse to create virtual factories, simulate different scenarios, and collaborate with remote teams.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing, which involves processing data closer to the source, will become increasingly important in smart manufacturing. Edge computing can reduce latency, improve real-time decision-making, and enhance security.
- AI-Powered Automation: AI will play an even greater role in automating tasks and optimizing processes in smart manufacturing. We can expect to see more sophisticated robots and autonomous systems on the factory floor.
- The Convergence of IT and OT: The convergence of IT (Information Technology) and OT (Operational Technology) will be crucial for realizing the full potential of smart manufacturing. This convergence will enable seamless data flow and communication between different systems.
- The Development of New Business Models: Smart manufacturing will enable manufacturers to develop new business models, such as servitization, where they offer services rather than just products.
Conclusion:-
Smart manufacturing is transforming the manufacturing landscape, enabling companies to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. While implementing smart manufacturing solutions can be challenging, the benefits are significant. By developing a clear vision and strategy, investing in the right technologies, and fostering a culture of innovation, manufacturers can successfully embrace the smart manufacturing revolution and position themselves for success in the digital age. The future of manufacturing is smart, and those who embrace this transformation will be the leaders of tomorrow.