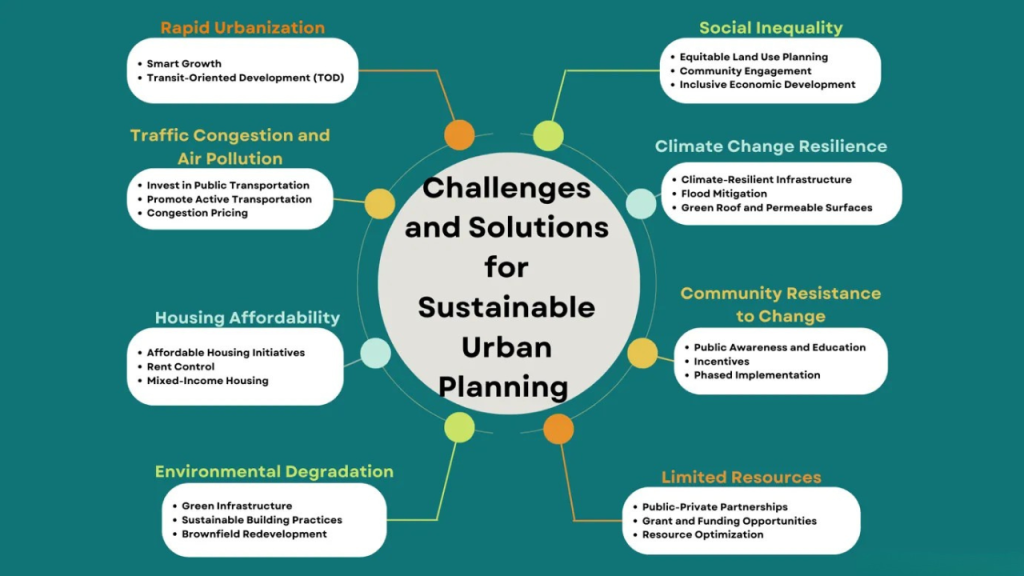
They’re the pulsating hearts of our world, Sustainable Cities the epicenters of innovation, culture, and economic growth. But they’re also facing unprecedented challenges, from the suffocating grip of pollution and the escalating threat of climate change to the growing disparities in resource access and the constant pressure of rapid population growth. Building sustainable cities isn’t just a trendy buzzword; it’s a critical imperative for the future of humanity.
We’re not talking about some utopian fantasy where everyone lives in vertical gardens and commutes by solar-powered zeppelin. Sustainability in urban contexts is about finding practical, actionable solutions that balance the needs of people, the planet, and prosperity. It’s about building resilient communities that can withstand the pressures of the 21st century and beyond.
So, how do we get there? Sustainable Cities Let’s dive into seven powerful strategies that can pave the way for thriving, eco-friendly urban centers:
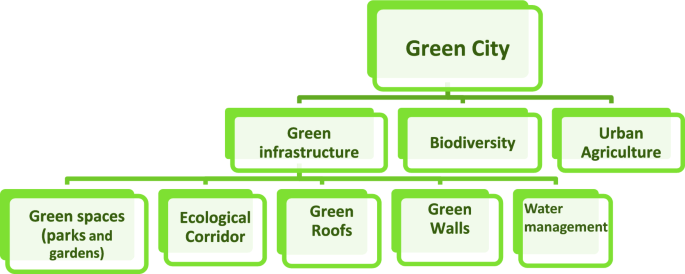
1. Embracing Green Infrastructure: Nature’s Solutions to Urban Problems
Think of green infrastructure as nature’s gift to the city. It’s about integrating natural systems into the urban fabric to tackle a myriad of challenges Sustainable Cities.
Instead of relying solely on concrete and steel, we can harness the power of plants, soil, and water to create more resilient and livable spaces.
Green Roofs and Walls: These living blankets not only reduce building energy consumption by providing insulation but also absorb rainwater, Sustainable Cities mitigate the urban heat island effect, and create habitats for wildlife.
Imagine a city where buildings are covered in lush vegetation, transforming concrete jungles into verdant oases.
Urban Forests and Parks: More than just aesthetic amenities, urban forests and parks act as vital carbon sinks, purify the air, and reduce stormwater runoff.
They provide spaces for recreation and relaxation, improving the mental and physical well-being of residents.
Rain Gardens and Bioswales: These strategically designed landscapes capture and filter stormwater, reducing flooding and improving water quality.
They mimic natural hydrological processes, allowing water to slowly infiltrate the ground instead of rushing into storm drains.
Restoring Urban Wetlands: Wetlands are natural sponges that absorb excess water, reducing flood risks. They also filter pollutants, provide habitat for diverse species, and offer recreational opportunities.
By embracing green infrastructure, we can create cities that are not only more sustainable but also more beautiful, healthier, and more enjoyable to live in Sustainable Cities.

2. Prioritizing Sustainable Transportation: Moving People, Not Just Cars
The dominance of private automobiles has led to traffic congestion, air pollution, and a decline in public health.
Sustainable transportation is about shifting the focus from cars to people, creating efficient and accessible alternatives that reduce our reliance on fossil fuels Sustainable Cities.
Investing in Public Transportation: High-quality, reliable, and affordable public transportation systems are crucial for reducing car dependency. This includes buses, trams, light rail, and subways.
Promoting Active Transportation: Walking and cycling are not only healthy and environmentally friendly but also cost-effective modes of transportation.
Cities need to invest in safe and well-connected pedestrian and cycling infrastructure Sustainable Cities.
Creating Transit-Oriented Development (TOD): TOD focuses on building mixed-use communities around public transportation hubs, reducing the need for long commutes and promoting walkability.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) and Alternative Fuels: While not a silver bullet, the transition to EVs and other alternative-fuel vehicles can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
Shared Mobility Solutions: Car-sharing, bike-sharing, and ride-hailing services can provide flexible and convenient transportation options, reducing the need for individual car ownership.
By reimagining our transportation systems, we can create cities that are less congested, less polluted, and more accessible to everyone.
3. Fostering Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy: Powering Cities Sustainably
Cities are major consumers of energy, and the traditional reliance on fossil fuels is a major contributor to climate change. Sustainable cities need to transition to energy-efficient buildings and renewable energy sources.
Building Energy Efficiency: Implementing stricter building codes, retrofitting existing buildings, and promoting energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Renewable Energy Generation: Investing in solar, wind, and geothermal energy can provide clean and sustainable power for cities.
Decentralized energy generation, such as rooftop solar panels, can also increase energy resilience.
Smart Grids and Energy Storage: Smart grids can optimize energy distribution and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively.
Energy storage technologies, such as batteries, can help to balance supply and demand.
Waste-to-Energy: Converting municipal solid waste into energy can reduce landfill waste and provide a sustainable source of power.
By embracing energy efficiency and renewable energy, we can create cities that are powered by clean and sustainable sources, reducing our carbon footprint and improving air quality.
4. Implementing Smart City Technologies: Using Data to Drive Sustainability
Smart city technologies can play a vital role in improving urban efficiency, resource management, and citizen engagement. By leveraging data and technology, cities can make more informed decisions and create more sustainable solutions.
Smart Sensors and Monitoring: Sensors can collect data on air quality, water quality, traffic flow, and energy consumption, providing valuable insights for urban planning and management.
Data Analytics and Visualization: Analyzing data can help cities identify patterns, trends, and areas for improvement. Visualizing data can make it easier for citizens and policymakers to understand complex issues.
Digital Platforms for Citizen Engagement: Online platforms can facilitate communication between citizens and government, enabling residents to report issues, provide feedback, and participate in decision-making Sustainable Cities.
Smart Waste Management: Sensors can monitor waste levels in bins, optimizing collection routes and reducing fuel consumption.
Smart Water Management: Sensors can detect leaks and monitor water consumption, helping to conserve water resources.
By leveraging smart city technologies, we can create cities that are more efficient, responsive, and sustainable.
5. Promoting Sustainable Consumption and Production: Reducing Our Ecological Footprint
Reducing Consumption: Promoting sustainable lifestyles, such as reducing consumption of single-use plastics and fast fashion, can help to reduce our ecological footprint.
Promoting Sustainable Production: Supporting businesses that adopt sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing waste, can help to create a more circular economy.
Reducing Food Waste: Food waste is a major problem in cities. Implementing food waste reduction programs, such as composting and food donation, can help to reduce waste and conserve resources.
Promoting the Sharing Economy: Sustainable Cities Sharing resources, such as tools, appliances, and vehicles, can reduce the need for individual ownership and promote sustainable consumption.
Local Production and Consumption: Supporting local businesses and farmers can reduce transportation emissions and promote sustainable agriculture.
By promoting sustainable consumption and production, we can create cities that are more resource-efficient and less wasteful.


excellent
wonderful!
super!
good!
Its like you read my mind! You seem to understand so
much approximately this, such as you wrote the e-book
in it or something. I think that you just could do
with some p.c. to power the message home a bit, but other than that, this is great blog.
A great read. I will certainly be back.
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and
wished to say that I have really enjoyed surfing around your weblog posts.
After all I will be subscribing to your feed and
I hope you write again very soon!
At this time I am ready to do my breakfast, once having my breakfast coming again to read further news.
Pretty! This was an extremely wonderful post.
Thank you for providing this information.
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your site and
in accession capital to assert that I get actually
enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
Very shortly this web site will be famous amid all blogging and site-building people, due to it’s good content